- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
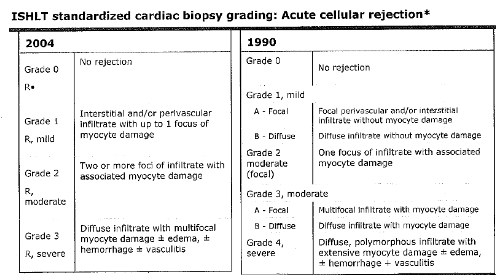
Rejection usually occurs in the days weeks or months after the transplant although it. The most common type of heart transplant rejection is called acute cellular rejection.
 Imaging In Heart Transplant Patients Sciencedirect
Imaging In Heart Transplant Patients Sciencedirect
2172021 The blockage of the vessels is the process that ultimately causes the transplanted heart to fail.
Heart transplants rejection. Understanding Heart Transplant Rejection. Through 180 days 17 of 22 NAT recipients 77 had a repeat rejection biopsy vs 12 of 28 NAT- recipients 43 p 002. This happens when your T-cells part of your immune system attack the cells of your new heart.
The first successful organ transplant performed in 1954 by Joseph Murray involved identical twins and so no rejection was observedOtherwise the number of mismatched gene variants namely alleles encoding cell surface molecules called major histocompatibility complex MHC classes I and II correlate with the rapidity and severity of transplant rejection. Unfortunately immunosuppression is a double-edged sword. Negative low-grade and high-grade ACR in 84 12 and 4 respectively vs 96 3 and 1 respectively in the NAT- group p 003.
Immune cells can attack the new heart. When a person gets a heart transplant the bodys immune system reacts. 5132019 Some people must consider a second heart transplant if rejection or allograft vasculopathy develops.
Immune cells can attack the new heart. 412021 Reverse-order heart-liver transplant helps prevent rejection for highly sensitized patients. Medicine can help to prevent this.
But in many cases rejection can still happen. Guidelines identifying potential HTx candidates were updated in 2016 by International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantatio. The success of heart transplantation in the 1980s was enabled by the ability to diagnose rejection by transjugular right ventricular endomyocardial biopsy.
1132021 The new blood test may be able to detect rejection as early as 28 days after heart transplantation and at least three months before rejection is detectable using heart tissue biopsy. Medicine can help to prevent this. This is where the immune system recognises the transplanted heart as foreign and attacks it.
When a person gets a heart transplant the bodys immune system reacts. Why heart transplant rejection happens. These results demonstrate a relative loss of high-frequency SA-ECG components in patients undergoing cardiac transplant rejection and suggest that the SA-ECG may be useful in the noninvasive evaluation of cardiac transplant rejection.
But in many cases rejection can still happen. It is this chronic rejection that is the major limiting factor for the long-term success of heart transplantation. Understanding Heart Transplant Rejection.
NAT biopsies demonstrated disparity of ACR distribution. Also while current heart biopsies are only performed in hospitals specimens for the new blood test can be collected at almost any commercial blood-collecting center. It happens most often in the first 3 to 6 months after transplant.
Rejection is a normal reaction of the body to new tissue put in or on the body. A person is less likely to survive when this interval is short ie. The incidence of any rejection between discharge and one year has decreased from 30 percent for primary transplants in 2004 to 2006 to 25 percent in 2010 to 2011 1.
Heart Transplantation Rejection Heart transplantation HTx is a procedure limited to patients with end-stage heart failure HF who remain symptomatic despite being on optimal medical and device therapy. All too often patients with high levels of antibodies face major challenges getting a transplant. Rejection is a normal reaction of the body to new tissue put in or on the body.
One of the most common complications of a heart transplant is rejection of the donor heart. Survival after heart retransplantation is related to the time interval between the first transplant and the retransplant. Slightly more than 2 percent of heart transplant cases are retransplants every year.
Despite the use of potent immunosuppressive agents both immediately after cardiac transplantation and during long-term maintenance acute rejection remains an important problem.
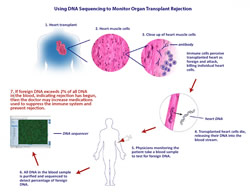
 Improving The Detection Of Heart Transplant Rejection With Dna Sequencing
Improving The Detection Of Heart Transplant Rejection With Dna Sequencing
 T1 And Extracellular Volume Data For Heart Transplant Patients Download Table
T1 And Extracellular Volume Data For Heart Transplant Patients Download Table
 Building A Tissue Based Molecular Diagnostic System In Heart Transplant Rejection The Heart Molecular Microscope Diagnostic Mmdx System The Journal Of Heart And Lung Transplantation
Building A Tissue Based Molecular Diagnostic System In Heart Transplant Rejection The Heart Molecular Microscope Diagnostic Mmdx System The Journal Of Heart And Lung Transplantation
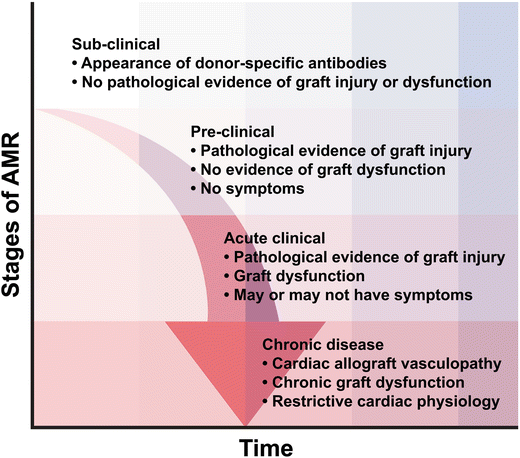 Heart Transplantation And Antibody Mediated Rejection Springerlink
Heart Transplantation And Antibody Mediated Rejection Springerlink
 Heart Transplant Rejection Causes Symptoms And Prevention
Heart Transplant Rejection Causes Symptoms And Prevention
 5 Facts To Keep In Mind About Heart Transplant Rejection Smallbeats Heart Transplant Transplant Rejection
5 Facts To Keep In Mind About Heart Transplant Rejection Smallbeats Heart Transplant Transplant Rejection
 Heart Transplantation At 50 The Lancet
Heart Transplantation At 50 The Lancet
Cardiac Transplantation Update On A Road Less Traveled Ochsner Journal
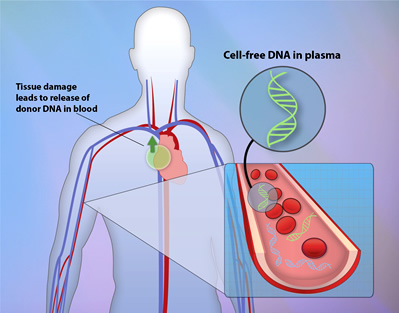
 Using Dna Sequencing To Monitor Organ Transplant Rejection
Using Dna Sequencing To Monitor Organ Transplant Rejection
 Heart Transplantation Circulation
Heart Transplantation Circulation
 Cardiac Transplantation Current Outcomes And Contemporary Controversies Sciencedirect
Cardiac Transplantation Current Outcomes And Contemporary Controversies Sciencedirect
 Evolving Areas In Heart Transplantation Sciencedirect
Evolving Areas In Heart Transplantation Sciencedirect
 Antibody Mediated Rejection In Cardiac Transplantation Emerging Knowledge In Diagnosis And Management Circulation
Antibody Mediated Rejection In Cardiac Transplantation Emerging Knowledge In Diagnosis And Management Circulation
Comments
Post a Comment